Why did durumis change from 38 languages to 18?
While researching to purchase plugins, I discovered that managing multilingual websites costs far more than anticipated!


The estimated cost of publishing one article is approximately 1,000 won. Interpreted differently, this means that for durumis to remain sustainable, each durumis user needs to generate at least 1,000 won or more in revenue per article published. However, are users of durumis, including myself, creating articles worth more than 1,000 won?
(Incorrect content corrected!)
durumis handles 18 languages, but translates only 17. (1 + 17 = 18)
Secondly, I operate three WordPress sites with an annual hosting cost of approximately 150,000 won. However, durumis uses significantly more expensive hosting.


Minimum = 800,000 won
Maximum = 4,600,000 won
Roughly calculating with the median value, it's approximately 2,700,000 won.
Can durumis cover its server costs with its current operating method?
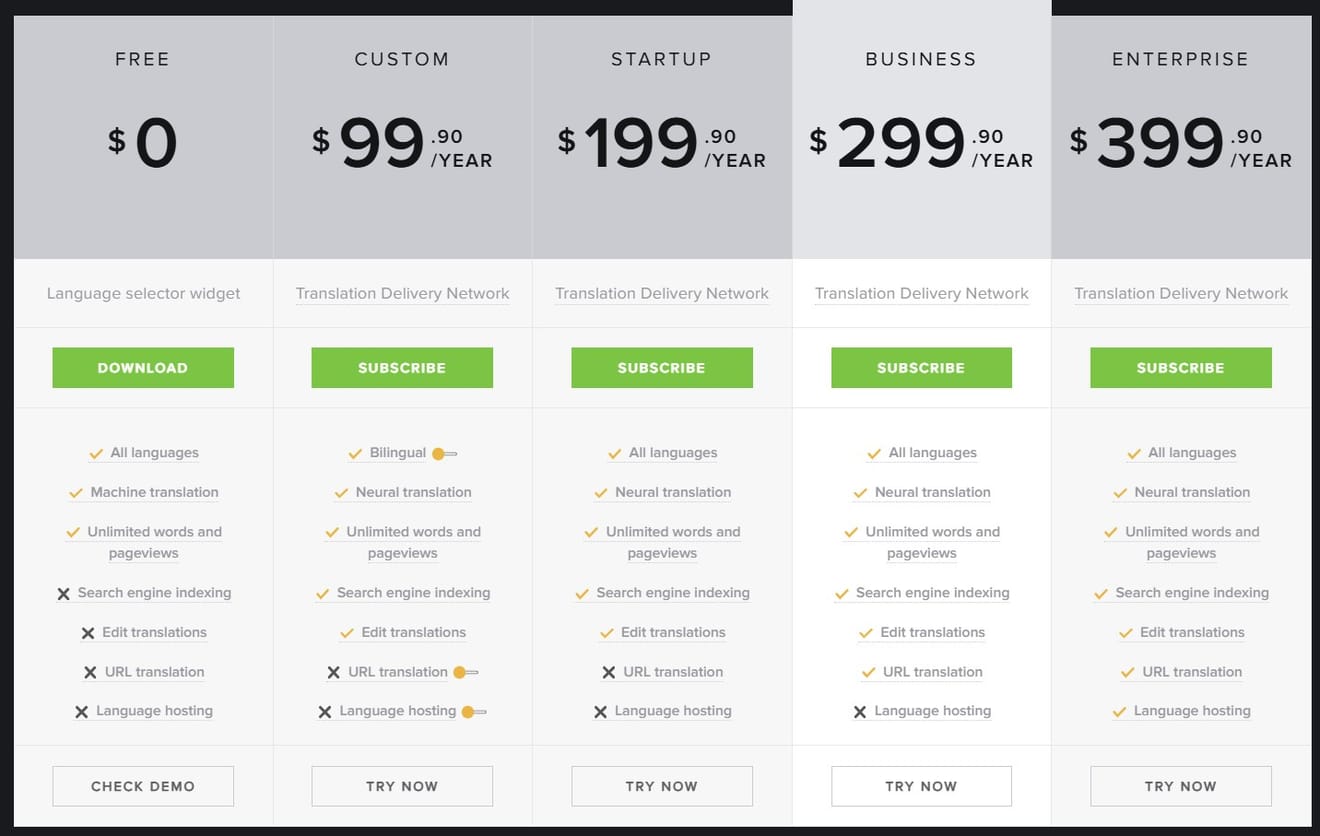
While calculating durumis' server and translation costs, another question arose. How can the GTranslate plugin provide unlimited translation services with subscription fees of $99, $199, $299, and $399 per year?It's quite intriguing that this is possible while using the Google API without possessing its own AI translation technology. I'm curious about the secret of this business model, and I believe that the answer to this question is a crucial challenge that durumis must address.
So what is GTranslate's competitive advantage?
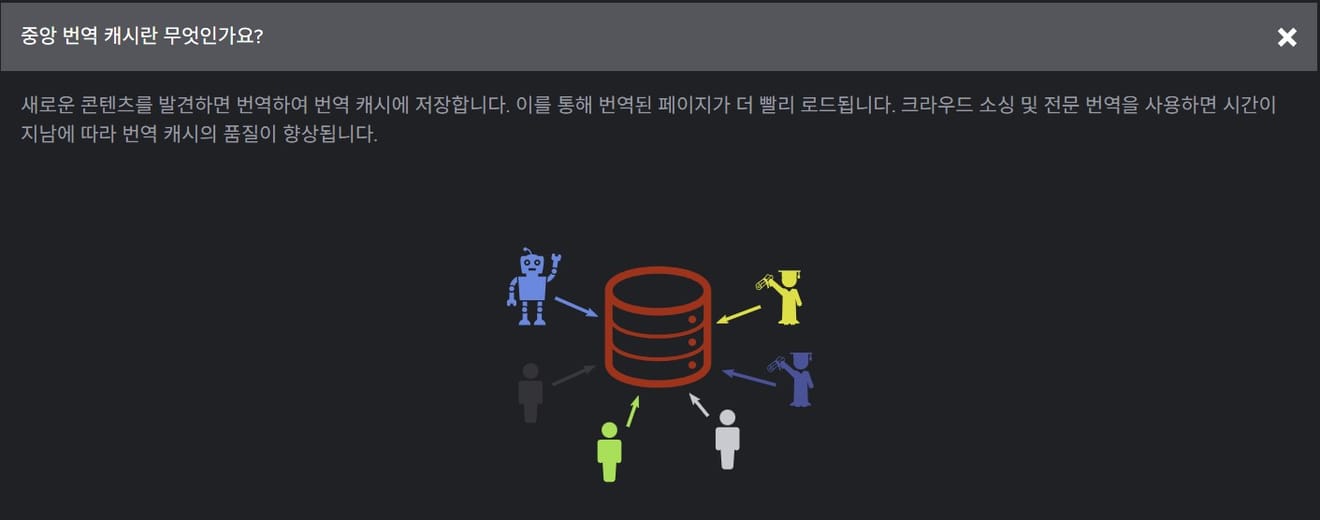
It's the Central Translation Cache technology. The Central Translation Cache is a system designed to efficiently manage multilingual content. Simply put, it's a method of storing translated text and retrieving it as needed.This eliminates wasted time on repeatedly translating the same text and maintains consistent translation quality. Most importantly, it doesn't require payment! This is particularly useful for services that need to provide multiple languages simultaneously, such as global websites or apps.
This system works by first checking the central translation cache when a new text translation request comes in. If the translated content is already stored, it's retrieved and used immediately. Conversely, if it's not in the cache, the Google AI translation engine processes it. The translated result is then stored in the cache, allowing for immediate retrieval without re-translation when the same text is encountered later.
The benefit of this method is the efficient reuse of translations! For example, when operating multilingual websites, the same text often appears repeatedly. Instead of translating this anew each time, storing it once in the cache allows for continuous use, saving time and costs. Furthermore, centralized translation management ensures that the same text always results in the same translation, increasing consistency and providing a cleaner user experience.
This technology is used in various industries. For example, large-scale e-commerce platforms need to provide large amounts of text, such as product descriptions and reviews, in multiple languages. Using a central translation cache improves operational efficiency. It also plays a crucial role in tools such as translation management systems (TMS) and translation memories (TM), and it's useful in translating user interfaces (UI) for mobile applications.
However, operating a central translation cache presents several challenges. First, the same text may require different translations depending on the context, requiring careful management. For instance, even a single word can have different meanings depending on the user's cultural background or context. Second, because the central translation cache stores large amounts of text data, storage management and system performance optimization are crucial. Finally, when translations are updated, care must be taken to prevent conflicts between new translation results and existing data during the cache data update process.
In conclusion, the central translation cache is a key technology in managing multilingual content.It automates translation tasks and increases efficiency while maintaining quality and consistency. The central translation cache is particularly useful in environments requiring large-scale translation tasks and is likely to be used in more industries as it continues to develop.
Comments0